Marketing, Distribution, and Quality Control in the Milk Industry

Introduction to Milk Marketing and Distribution
Milk is a staple in many diets around the world. Its nutritional benefits and versatility make it a popular choice among consumers. However, effectively marketing and distributing milk requires careful planning and execution. This article explores the marketing strategies, distribution channels, common defects, and quality control measures in the milk industry.
Focus Keyphrase: Milk Marketing and Distribution
Slug: milk-marketing-distribution
Meta Description: Discover effective marketing strategies, distribution channels, and quality control measures in the milk industry. Learn about common defects and how to ensure high-quality milk.
Keyphrase Synonyms:
- Dairy Product Marketing
- Milk Distribution Strategies
- Quality Control in Milk
- Milk Supply Chain Management
The Importance of Milk Marketing
Marketing plays a crucial role in the dairy industry. It helps create awareness about milk products and their benefits. Here are some effective marketing strategies:
1. Highlight Nutritional Benefits
Milk is rich in calcium, vitamins, and protein. Marketing campaigns should emphasize these benefits. Use social media, blogs, and advertisements to educate consumers about the health advantages of milk.
2. Promote Versatility
Milk is not just a beverage; it is also an ingredient in many recipes. Highlighting its versatility can attract a broader audience. Share recipes that incorporate milk in cooking and baking.
3. Engage with Consumers
Building a relationship with consumers is essential. Use social media platforms to engage with your audience. Share stories about local farms, sustainability practices, and the journey of milk from farm to table.
Distribution Channels for Milk
The distribution of milk requires a well-planned strategy to ensure freshness and quality. Here are the key distribution channels:
1. Direct Distribution
Dairy farms can sell milk directly to consumers through farm stands or local markets. This method allows farmers to build a loyal customer base and ensure product freshness.
2. Retail Distribution
Supermarkets and grocery stores are primary distribution points for milk. Establishing partnerships with retailers is crucial. Ensure that milk is stored in refrigerated sections to maintain quality.
3. Online Sales
With the rise of e-commerce, online sales of milk and dairy products are becoming popular. Offering delivery services can attract tech-savvy consumers who prefer shopping from home.
4. Food Service Distribution
Restaurants, cafes, and schools are significant consumers of milk. Establishing contracts with food service providers can create a steady demand for milk products.
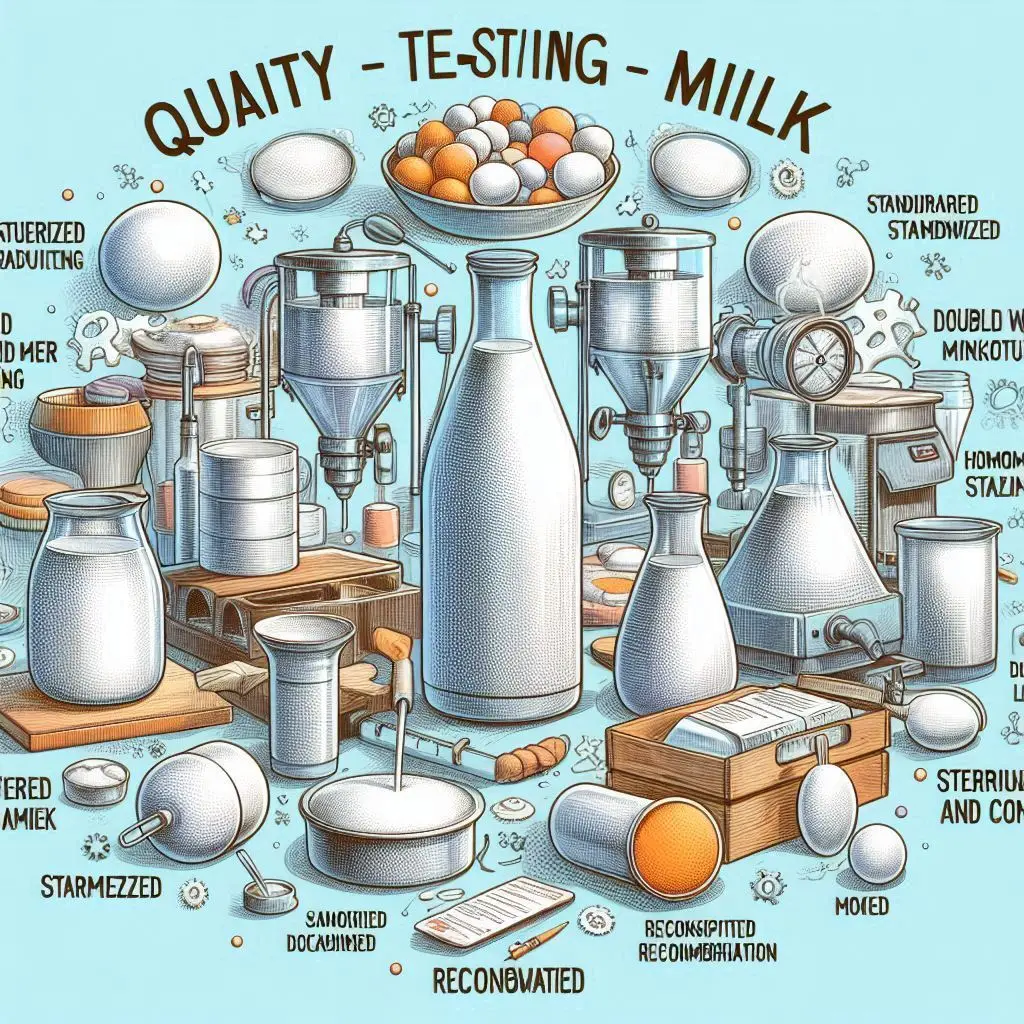
Maintaining Quality Control in Milk
Quality control is vital in the milk industry to ensure safety and freshness. Here are some essential quality control measures:
1. Temperature Control
Milk should be stored and transported at low temperatures to prevent spoilage. The ideal temperature for storing milk is below 4°C (39°F). Implementing strict temperature controls throughout the supply chain is essential.
2. Regular Testing
Conducting regular microbiological testing helps identify contamination. Testing for pathogens like E. coli and Listeria ensures that milk is safe for consumption.
3. Hygiene Practices
Maintaining cleanliness in processing facilities is crucial. Regular sanitation of equipment and surfaces prevents cross-contamination. Train employees on proper hygiene practices to minimize risks.
4. Quality Assurance Protocols
Implementing quality assurance protocols helps monitor the entire production process. This includes tracking milk from the farm to the consumer. Regular audits can help identify areas for improvement.
Common Defects in Milk and Their Control
Despite best efforts, defects can still occur in milk. Understanding these defects and how to control them is essential for maintaining quality.
1. Microbial Spoilage
Microbial spoilage is a common issue in milk. Bacteria can multiply rapidly if proper temperature controls are not maintained. To combat this, ensure that milk is pasteurized and stored correctly.
2. Physical Defects
Physical defects, such as curdling or off-flavors, can occur due to improper handling. Educating staff on proper handling techniques can reduce the risk of these defects.
3. Chemical Changes
Chemical changes can affect the taste and quality of milk. Exposure to light or prolonged storage can lead to off-flavors. Use opaque packaging to protect milk from light and ensure timely distribution.
Conclusion
Effective marketing, distribution, and quality control are crucial for success in the milk industry. By highlighting the nutritional benefits and versatility of milk, engaging with consumers, and maintaining strict quality control measures, dairy producers can ensure the delivery of high-quality milk products. Understanding and addressing common defects will further enhance consumer trust and satisfaction.
For more pearls of Vets Wisdom:
https://wiseias.com/partitioning-of-food-energy-within-animals/




Anyone know where to reliably get the yolo247download? Heard some dodgy stuff about unofficial versions. Found it here: yolo247download Seems legit!
Looking for a new betting site and skysportsbettingg caught my eye. Anyone had any good experiences with them? Thinking of using skysportsbettingg for the upcoming games.
Heard khelraja is gaining popularity. Is it as good as they say? Thinking of signing up. Found the site at khelraja