Oblique Fractures in Animals

Introduction
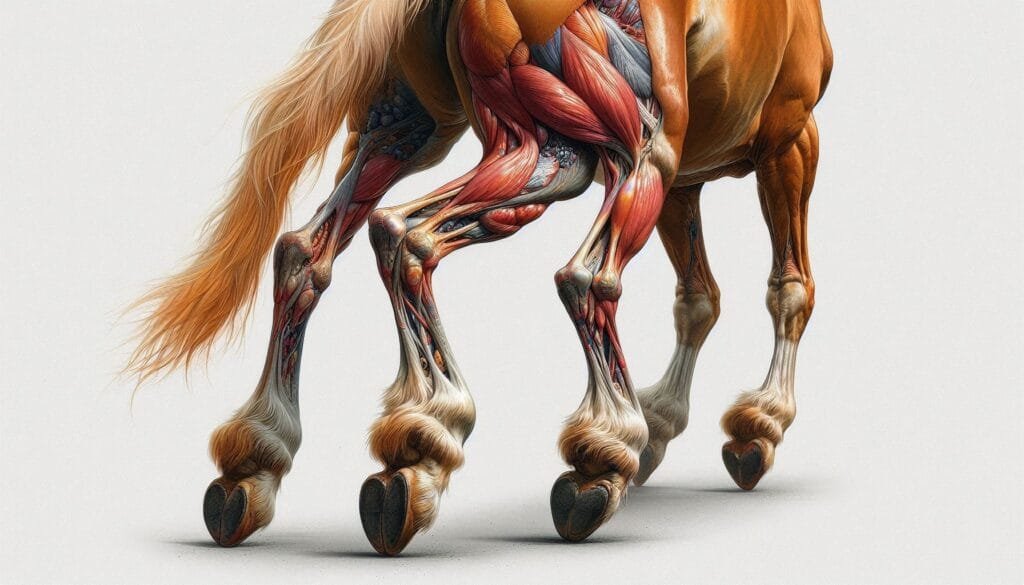
Oblique fractures are a specific type of bone break characterized by an angled or diagonal fracture line across the bone. These fractures commonly occur in the long bones of farm and domestic animals, such as cattle, horses, dogs, and cats. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies for oblique fractures is crucial for veterinarians and animal caregivers to ensure optimal recovery and animal welfare.
Causes of Oblique Fractures in Animals
Oblique fractures typically result from trauma that applies force at an angle to the bone. Common causes include:
- Falls: Animals that slip or fall from heights may sustain oblique fractures due to the angled impact on their limbs. For instance, cattle and buffaloes often suffer fractures from slipping and falling on hard floors.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Vehicle Accidents: Collisions with vehicles can impart significant angular force, leading to oblique fractures, especially in free-ranging animals.
- Kicks or Blows: Animals struck by other animals or objects may experience oblique fractures due to the direction and magnitude of the force applied.
Symptoms of Oblique Fractures
Recognizing the signs of an oblique fracture is essential for timely intervention. Symptoms may include:
- Lameness: Animals may exhibit sudden limping or an inability to bear weight on the affected limb.
- Swelling and Pain: The fracture site often becomes swollen, tender, and painful to touch.
- Abnormal Limb Position: The affected limb may appear misaligned or at an unusual angle.
- Crepitus: A grating sound or sensation may be felt when the fractured bone ends rub against each other.
Diagnosis of Oblique Fractures
Accurate diagnosis involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging techniques:
- Physical Examination: Veterinarians assess the animal’s gait, limb positioning, and pain response to identify potential fractures.
- Radiography (X-rays): X-rays are the primary diagnostic tool to visualize the fracture’s location, orientation, and severity. They help distinguish oblique fractures from other types, such as transverse or spiral fractures.
todaysveterinarypractice.com - Advanced Imaging: In complex cases, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may provide detailed information about the fracture and surrounding tissues.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach depends on factors like the animal’s species, size, age, overall health, and the fracture’s characteristics.
Conservative Management
- Rest and Immobilization: Small animals or fractures with minimal displacement may heal with strict rest and external support, such as splints or casts.
acvs.org - Pain Management: Analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation during the healing process.
Surgical Intervention
- Internal Fixation: Surgical methods, such as plating or intramedullary pinning, stabilize the fracture internally, promoting proper alignment and faster healing.
todaysveterinarypractice.com - External Fixation: External devices, like fixator frames, stabilize the fracture externally and are often used in large animals or when internal fixation isn’t feasible.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Post-treatment care is vital for successful healing:
- Controlled Exercise: Gradual reintroduction of movement prevents joint stiffness and muscle atrophy.
- Physical Therapy: Techniques like massage, hydrotherapy, and controlled exercises enhance mobility and strength.
- Monitoring: Regular veterinary check-ups ensure the fracture is healing correctly and detect any complications early.
Prevention Strategies
While not all fractures are preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Safe Housing: Ensure living areas are free from hazards that could cause slips or falls.
- Proper Handling: Use gentle and appropriate techniques when moving or restraining animals to prevent accidental injuries.
- Nutrition: Provide a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients to maintain bone health and strength.
Conclusion
Oblique fractures in the long bones of farm and domestic animals require prompt recognition and appropriate management to ensure optimal recovery. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and prevention strategies, veterinarians and animal caregivers can effectively address these injuries, enhancing the well-being and quality of life for affected animals.
For more pearls of Vets Wisdom:
Heritability: Methods and Applications

Responses