Ruminant Impaction in Cattle

Ruminant Impaction in Cattle: A Complete Guide
Ruminant impaction, also known as rumen impaction, is a serious condition affecting cattle where the rumen becomes blocked with indigestible materials like compacted feed, foreign objects, or hairballs. This condition can cause discomfort and even be fatal if not addressed promptly. Understanding how to diagnose, treat, and prevent ruminant impaction in cattle is essential for maintaining herd health.
What is Ruminant Impaction in Cattle?
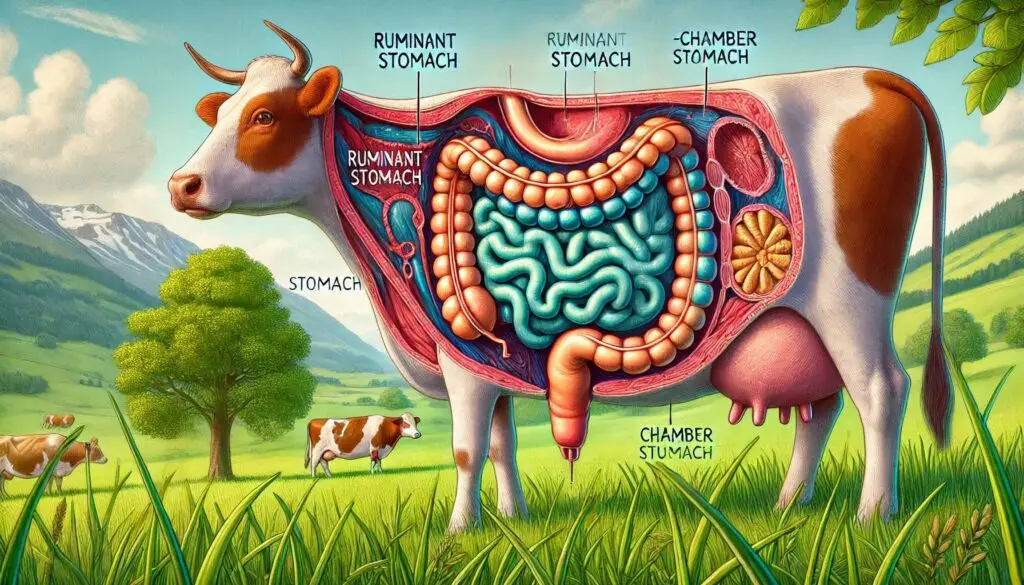
Ruminant impaction refers to the blockage of the rumen, the largest compartment of a cow’s stomach. The rumen plays a crucial role in digesting fibrous plant material, and when it becomes impacted, it can lead to serious health issues. Cattle with impaction may experience discomfort, reduced feed intake, and other signs of distress.
How Ruminant Impaction Occurs
Impaction occurs when the rumen is filled with indigestible substances like compacted feed, foreign objects, or even hairballs. These materials can form a mass that disrupts normal rumen function. Cattle are especially susceptible when they ingest poor-quality feed or are fed insufficient fiber.
For more details on the mechanisms of ruminant digestion and how feed quality impacts digestive health, check out this detailed article on ruminant digestive systems.
Clinical Signs of Ruminant Impaction in Cattle
Identifying Symptoms of Ruminant Impaction
Veterinarians rely on various symptoms to diagnose ruminant impaction in cattle. The most common clinical signs include:
- Reduced Feed Intake: Cattle may refuse to eat or show signs of decreased appetite.
- Distended Left Flank: A bloated or swollen left side can be an indication of rumen blockage.
- Decreased Rumen Contractions: A healthy rumen should contract regularly. In cases of impaction, these contractions decrease or stop altogether.
- Signs of Discomfort: The cow may appear restless, grunt, or show signs of pain.
Recognizing these early signs is critical. If you observe any of these symptoms in your cattle, seek veterinary assistance immediately.
Why Early Diagnosis is Crucial
If left untreated, rumen impaction can lead to severe dehydration, malnutrition, and even death. By diagnosing the condition early, veterinarians can begin treatment before the situation becomes critical.
For more on how to identify digestive health issues in cattle, visit this veterinary guide.
Diagnosis of Ruminant Impaction
Physical Examination
A rectal examination is often the first step in diagnosing rumen impaction. During this procedure, veterinarians can palpate the abdomen and feel for a firm mass or blockage in the rumen. This hands-on approach helps veterinarians assess the severity of the impaction and determine the appropriate course of action.
Ultrasonography for Rumen Impaction
Another valuable diagnostic tool is ultrasound. Ultrasonography allows veterinarians to visualize the rumen and identify the size and location of the impaction. The images can help guide treatment decisions and ensure that the right methods are used to relieve the blockage.
To learn more about diagnostic methods for cattle, including ultrasound, check out this veterinary ultrasound guide.
Blood Tests and Additional Diagnostics
In some cases, blood tests may be required to assess the overall health of the animal and rule out other conditions. Blood work can show signs of dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, or systemic infection.
Treatment of Ruminant Impaction
Oral Fluids and Electrolytes
One of the first treatments for ruminant impaction is the administration of oral fluids. Electrolyte solutions or mineral oil are often given to help soften and break down the impaction. These fluids can assist in restoring normal rumen function by aiding the digestion of compacted feed and foreign objects.
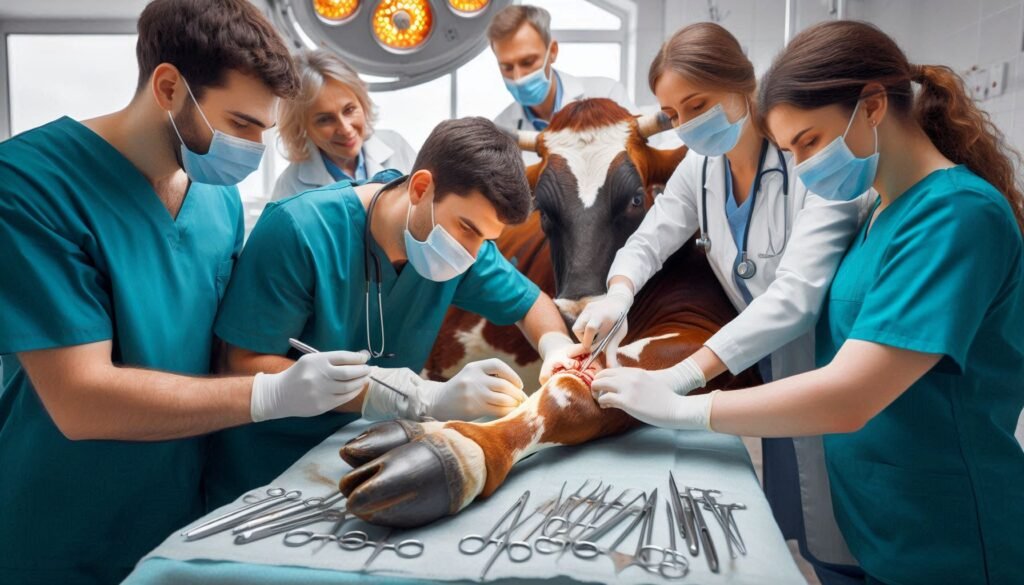
Rumenotomy: A Surgical Solution
In severe cases, a rumenotomy, or surgical procedure, may be necessary. This surgery involves making an incision into the rumen to manually remove the impaction. While it is a more invasive procedure, it can be life-saving for cattle with severe or persistent blockages.
For a more in-depth look at the rumenotomy procedure, you can refer to this surgical procedure guide.
Laxatives to Facilitate Rumen Contractions
Administering laxatives such as magnesium sulfate can help stimulate rumen contractions. These contractions help push the impacted material through the digestive system. While laxatives can be an effective non-surgical treatment, they are typically used in conjunction with other methods.
Dietary Adjustments for Prevention
Preventing ruminant impaction involves making dietary adjustments that improve rumen health. Some strategies include:
- Providing higher-quality feed that is easier to digest.
- Increasing the fiber content in the diet to promote normal rumen motility.
- Regularly monitoring feed quality to avoid introducing harmful materials into the rumen.
For more insights into managing cattle diets and improving rumen health, check out this article on cattle nutrition.
Pain Management for Affected Cattle
Pain relief is an important aspect of treatment. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort. By managing pain, cattle are better able to recover and resume normal feeding behaviors.
Preventing Ruminant Impaction in Cattle
The Role of Feed Management
One of the best ways to prevent rumen impaction is by focusing on proper feed management. Ensuring cattle have access to high-quality forage and adequate amounts of fiber will reduce the risk of impaction. If necessary, introduce feed additives to help maintain rumen health.
Routine Veterinary Checkups and Monitoring
Regular veterinary checkups play a crucial role in identifying potential risks for ruminant impaction. Early intervention during routine examinations can catch problems before they escalate.
Maintaining Hydration and Access to Clean Water
Cattle that are not adequately hydrated are at a higher risk for digestive problems. Ensuring constant access to fresh water helps maintain healthy rumen function and prevents impactions from developing.
Conclusion
Ruminant impaction in cattle is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing the symptoms early, using appropriate diagnostic tools, and employing effective treatment methods such as oral fluids, rumenotomy, and dietary adjustments, you can ensure that your cattle stay healthy and free from digestive blockages. Preventive measures like proper feed management and regular veterinary checkups are essential to maintaining long-term rumen health in your herd.
For more on managing cattle health, visit the Merck Veterinary Manual.
More From Animal Diseases:
Niacin Deficiency in Birds




Responses