Vas Deferens in Bulls
Introduction
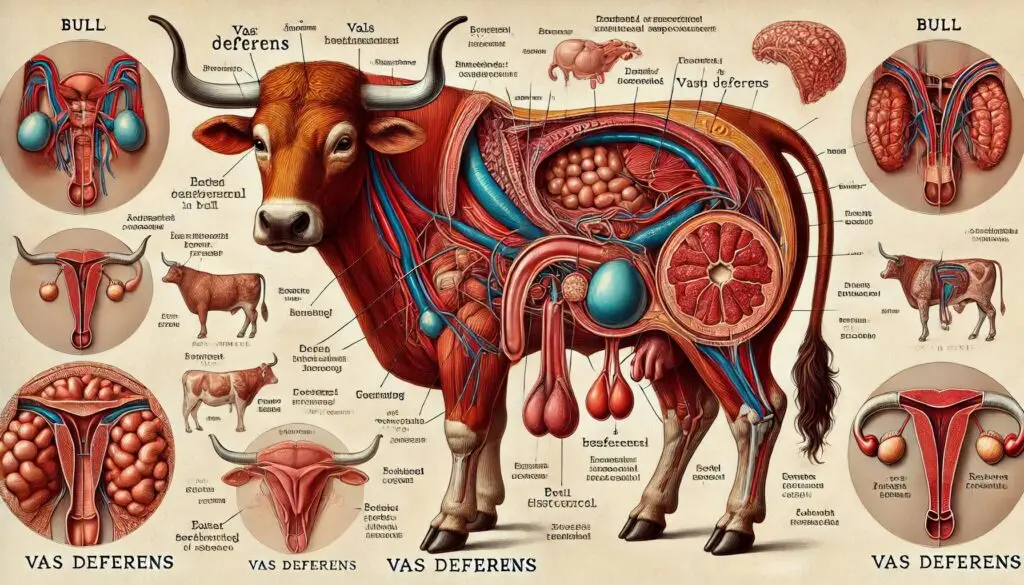
The vas deferens plays a vital role in the male reproductive system of bulls. Understanding its anatomy and function is crucial for anyone involved in cattle breeding or veterinary care. This article delves into the vas deferens, exploring its structure, function, and significance in bull reproduction.
Anatomy of the Vas Deferens
Structure Overview
The vas deferens is a muscular tube that connects the epididymis to the urethra. It is part of the male reproductive tract and is essential for sperm transport.
Key Components
- Epididymis: This coiled structure stores sperm produced in the testes.
- Inguinal Canal: The vas deferens passes through this canal as part of the spermatic cord.
- Seminal Vesicles: These glands contribute fluid to semen and are located near the vas deferens.
For more detailed information on the anatomy of male reproductive systems, you can visit The Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System.
Length and Location
In bulls, the vas deferens can be quite long, measuring about 60 to 70 cm. It runs from each testis through the inguinal canal and into the pelvic cavity. Understanding its location helps in diagnosing potential reproductive issues.
Function of the Vas Deferens
The primary function of the vas deferens is to transport sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
Sperm Transport Mechanism
When a bull ejaculates, smooth muscle contractions propel sperm through the vas deferens. This process is crucial for successful mating. The contractions are rhythmic and are influenced by hormonal signals.
For a deeper look into how sperm transport works, check out Sperm Transport Mechanisms.
Role in Semen Formation
As sperm travel through the vas deferens, they mix with fluids from accessory glands like the seminal vesicles and prostate gland. This mixture forms semen, which nourishes and protects sperm.
Seminal Vesicles Contribution
The seminal vesicles produce a significant portion of seminal fluid, providing fructose for energy. This energy source is vital for sperm motility.
Clinical Importance of the Vas Deferens
Understanding potential health issues related to the vas deferens can help prevent infertility in bulls.
Common Health Issues
- Epididymitis: Inflammation of the epididymis can block sperm transport.
- Vasectomy: This surgical procedure involves cutting or sealing the vas deferens to prevent sperm from entering the urethra.
For more information on epididymitis in bulls, refer to Epididymitis in Bulls.
Impact on Fertility
Blockages or infections can lead to reduced fertility or complete infertility. Regular veterinary check-ups can help identify these issues early.
Diagnostic Techniques
Veterinarians may use ultrasound or semen analysis to assess reproductive health. These techniques provide valuable insights into potential problems with the vas deferens or other parts of the reproductive system.
Management Practices for Healthy Reproduction
Maintaining reproductive health in bulls requires proper management practices.
Nutrition and Health Care
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health. Nutritional deficiencies can negatively impact sperm production and quality.
For guidance on bull nutrition, refer to Nutrition for Beef Cattle.
Breeding Management
Implementing effective breeding management practices can enhance fertility rates. Considerations include:
- Timing: Synchronizing estrus can improve breeding success.
- Teaser Bulls: Using teaser bulls helps detect estrus more effectively.
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups
Routine veterinary visits are essential for monitoring reproductive health. These check-ups can identify issues before they become serious problems.
Conclusion
The vas deferens is a crucial component of bull reproduction. Understanding its anatomy and function helps improve breeding practices and overall herd health. By focusing on nutrition, health care, and regular veterinary check-ups, cattle producers can enhance fertility outcomes.
More from Veterinary Anatomy:



Downloaded the Xoso66appapk! So far so good, seems pretty snappy. Gonna give it a whirl tonight. Def worth a download if you’re into this kinda thing: xoso66appapk
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.