Back to Course
1st Year BVSc & AH Course
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Crash Course
Animal Physiology3 Topics -
LPM9 Topics
-
Veterinary AnatomyAnatomy PPT
-
Unit 1 Introduction to anatomy and branches of anatomy6 Topics|6 Quizzes
-
Introduction to anatomy and branches of anatomy and descriptive terms used in anatomy and study of anatomical planes.
-
General Osteology, Arthrology and Myology
-
General Angiology, Neurology and Aesthesiology
-
Different surface regions, joint regions, Palpable Bony areas or prominences of the body of the animal
-
General Splanchnology
-
Principles and application of Radiography and Ultrasound for bones and soft tissues.
-
Introduction to anatomy and branches of anatomy and descriptive terms used in anatomy and study of anatomical planes.
-
Unit 2 Forelimb4 Topics|4 Quizzes
-
Unit 3 Head and neck5 Topics|5 Quizzes
-
Study of cranial and facial bones, Study of paranasal sinuses
-
Study of articulations and special ligaments, Study of teeth, palate and salivary glands
-
Study of cranial nerves, blood vessels sense organs and lymph nodes
-
Age determination by Dentition ,Importance of Cornual nerve
-
Sites for Tracheotomy, Esophagotomy and surgical approach to guttural pouches in horse.
-
Study of cranial and facial bones, Study of paranasal sinuses
-
Unit 4 Thorax4 Topics|4 Quizzes
-
Study of thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum of ox and differences in horse, dog, pig and fowl.
-
Study of joints, ligaments, blood vessels, nerves, and lymph nodes of thorax.
-
Study of organs of thorax, differences in between horse, dog, pig and fowl.
-
Study of pleura and mediastinum. Areas of auscultation and percussion of heart and lungs.
-
Study of thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum of ox and differences in horse, dog, pig and fowl.
-
Unit 5 Abdomen4 Topics|4 Quizzes
-
Study of bones, joints, special ligaments,blood vessels,and nerves of abdomen region
-
Study of peritoneal reflections, organs of digestive, urinary, male and female reproductive systems
-
Study of mammary glands, spleen, major veins, lymph vessels,and lymph nodes
-
Sites for Liver, Caecal Biopsies, Laparotomy, spleenectomy, Cystotomy Caesarean Operation, and paravertebral block.
-
Study of bones, joints, special ligaments,blood vessels,and nerves of abdomen region
-
UNIT 6 Hind limb and pelvis5 Topics|5 Quizzes
-
Study of bones of hind limb and pelvis
-
Study of joints, ligaments, blood vessels, lymph nodes and nerves
-
Study of pelvic peritoneal reflections, organs of digestive, urinary, reproductive systems
-
Boundaries of the inguinal canal and structures of the spermatic cord
-
Study of external genital organs. Sites for Tibial, Peroneal, Plantar and Pudic nerve blocks
-
Study of bones of hind limb and pelvis
-
UNIT 7 Cytology3 Topics|3 Quizzes
-
Unit 8 Introduction to embryology4 Topics|4 Quizzes
-
Introduction to embryology, gametogenesis, fertilization, cleavage , types of implantation
-
Placenta and its classification Formation of foetal membranes in mammals and birds
-
Study of development of organs of digestive system
-
Study of development of organs of respiratory, urinary, circulatory, lymphatic, nervous, reproductive systems
-
Introduction to embryology, gametogenesis, fertilization, cleavage , types of implantation
-
Most frequent asking Veterinary Anatomy Differences
-
Veterinary Anatomy spotting
-
VPB –111- VETERINARY PHYSIOLOGY -I (Blood, Cardiovascular, Excretory system and Body Fluids)Unit 1 Hematology36 Topics|36 Quizzes
-
Circulatory Systems
-
Blood
-
Plasma
-
Plasma Proteins
-
Serum
-
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) / Erythrocytes
-
Haematopoiesis
-
Erythropoiesis
-
Regulation of Red Blood Cell Production
-
Maturation of Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
-
Hematocrit, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, and Osmotic Fragility
-
Hemolysis
-
Hemoglobin
-
Transport, Storage, and Synthesis of Iron and Hemoglobin
-
Hemoglobin and Its Combination with Oxygen
-
Abnormal Hemoglobins / Hemoglobinopathies
-
Catabolism of Hemoglobin
-
Metabolism of Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
-
Variations in Shape, Size, and Count of RBCs
-
Blood Indices (Erythrocyte Indices)
-
Anemia
-
Polycythemia
-
Haemostasis
-
Mechanism of Platelet Plug Formation
-
Blood Coagulation
-
Mechanism of Blood Coagulation
-
Initiation of Coagulation
-
Prevention of Blood Clotting in the Normal Vascular System
-
Conditions That Cause Excessive Bleeding
-
Methods for Estimation of Hemoglobin
-
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
-
Basophils and Mast Cells
-
Monocytes
-
Lymphocytes
-
Reticuloendothelial System (Monocyte-Macrophage System)
-
Immunity
-
Circulatory Systems
-
Unit 2 Cardiology20 Topics|20 Quizzes
-
Cardiovascular Physiology
-
Anatomy of the Heart
-
Cardiac Muscle: Structure and Function
-
Conduction System of the Heart
-
Transmission of Cardiac Impulse
-
Action Potential in Pacemaker Cells (SA Node)
-
Excitation-Contraction Coupling in the Myocardium
-
Properties of Myocardium
-
Metabolism and Energetics of Working Myocardial Cells
-
Cardiac Cycle
-
Cardiac Sounds
-
Electrical Changes in the Heart
-
Common Lead Systems in Electrocardiography
-
ECG Waves, Segments, and Intervals
-
Stroke Volume (SV)
-
Determination of Cardiac Output
-
Regulation of Cardiac Output
-
Coronary Circulation
-
Regulation of Coronary Circulation
-
Echocardiography
-
Cardiovascular Physiology
-
Unit 3- Hemodynamics22 Topics|22 Quizzes
-
Blood Volume Versus Body Weight
-
Vascular Tone
-
Dynamic Parameters of Hemodynamics
-
Distribution of Blood in the Systemic Circulation
-
Blood Pressure
-
Factors Influencing Production and Maintenance of Blood Pressure
-
Cardiovascular Regulation
-
Control of Circulation by Nerves
-
Reflex Control of Circulation
-
Regulation of Blood Vessels by Hormones
-
Venous Circulation
-
Pulse
-
Capillary Circulation
-
Lymphatic System
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) and Synovial Fluid
-
Shock
-
Hypertension
-
Heart Failure
-
Pulmonary Circulation
-
Cerebral Circulation
-
Cutaneous Circulation
-
Circulation to Skeletal Muscles and Splanchnic Circulation
-
Blood Volume Versus Body Weight
-
Unit 2 DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS5 Topics|5 Quizzes
-
Morphological characteristic of mono gastric and poly gastric digestive system
-
Prehension, rumination, regulation of secretory function, enzymatic digestion in monogastric and fermentative digestion
-
Digestion & Respiration in birds
-
Functional morphology of respiratory apparatus. Mechanics of breathing
-
Transport of blood gases, Frictional resistance to air flow, airways smooth muscle contraction
-
Morphological characteristic of mono gastric and poly gastric digestive system
-
Physiology PPT
-
Physiology Previous year frequent asking questions
-
LPMLPM PPT
-
Unit 1 GENERAL LIVESTOCK MANAGEMENT15 Topics|15 Quizzes
-
Demographic Distribution of Livestock and Role in the Indian Economy
-
Problems and Prospects of the Livestock Industry in India
-
Common Animal Husbandry Terms (Glossary)
-
Body Conformation and Identification
-
Transportation of Livestock and Wild/Zoo Animals
-
Common Farm Management Practices
-
Introduction to Methods of Drug Administration
-
Common Vices of Animals and Their Prevention
-
Livestock Production Systems
-
Animal Holding and Land Holding Patterns in Different Agro-Climatic Zones
-
Organic Livestock Production
-
Judging and BCS for Body Parts of Livestock
-
Preparation of Animals for Show
-
Culling of Animals
-
Selection and Purchase of Livestock
-
Demographic Distribution of Livestock and Role in the Indian Economy
-
Unit 2 FODDER PRODUCTION AND CONSERVATION7 Topics|7 Quizzes
-
Importance of grasslands and fodder in livestock production
-
Agronomical Practices for fodder production
-
Important leguminous and non-leguminous fodders in different seasons
-
Soil and Water conservation and drainage of water for fodder production
-
Fodder production for small livestock units. Structures for storage of feeds and fodders
-
Scarcity fodders and preservation of green fodder
-
Recycling of animal washings and wastes in fodders production and use of recycle waste
-
Importance of grasslands and fodder in livestock production
-
Unit 3 LIVESTOCK PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT-RUMINANTS6 Topics|6 Quizzes
-
Housing systems Selection of site General principles affecting the design
-
Arrangements of the building to Indian conditions their characteristics, merits and demerits
-
Breeds of cattle and buffalo, Economic traits
-
General management and feeding practices of calves, heifers, pregnant, lactating and dry animals
-
Factors affecting quality and quantity of milk production Routine animal farm operations and labour management
-
Breeds of sheep and goat and their descriptions Breeding schedule and management of ram and buck
-
Housing systems Selection of site General principles affecting the design
-
Unit 4 ZOO ANIMALS PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT4 Topics|4 Quizzes
-
Taxonomy of important wild zoo animals. Status and conservation practices of wild life in India
-
Size and space requirement (dimension) of cubicles, enclosures of important wild zoo animals
-
Feeding habits, Restraining, capture, handling, physical examination of captive animals.
-
Classification of zoos, Acts and Rules, Organization interlinked to captive animals role and functioning.
-
Taxonomy of important wild zoo animals. Status and conservation practices of wild life in India
-
Unit 5 ANIMAL WELFARE5 Topics|5 Quizzes
-
Definition of animal welfare and ethics
-
Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PCA) Act, Welfare of animals during transportation.
-
Animal welfare in commercial livestock farming practices
-
Legal duties of veterinarians, Laws relating to offences affecting Public Health
-
Code of Conduct and Ethics for veterinarians the Regulations made under the Act
-
Definition of animal welfare and ethics
-
Unit 6 POULTRY PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT5 Topics|5 Quizzes
-
Indian poultry industry - Brief outline of the different segments
-
Description of indigenous fowls and their value, Brooding management, Housing Types.
-
Scavenging system of management, Cage management, Advantages and disadvantages
-
Management of growers and layers, Nutrient requirements and feed formulations
-
Breeding systems and methods of mating, Health care for common poultry diseases vaccination
-
Indian poultry industry - Brief outline of the different segments
-
UNIT 7 DIVERSIFIED POULTRY PRODUCTION AND HATCHERY MANAGEMENT4 Topics|4 Quizzes
-
UNIT 8 LABORATORY OR RABBIT OR PET ANIMAL PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT4 Topics|4 Quizzes
-
UNIT 9 SWINE OR EQUINE OR CAMEL, YAK AND MITHUN PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT6 Topics|6 Quizzes
-
Introduction and scope of swine farming
-
Housing and feeding of swine, Equine population of India and their utility
-
Care and routine management and Identification of breeds of horses
-
Vices of horses , Foaling and care of newborn, Colic and its prevention.
-
Common breeds of camel in India and their utility
-
Feeding and breeding of Mithun or Yaks.
-
Introduction and scope of swine farming
-
LPM Previous year frequent asking questions
Lesson 4,
Topic 3
In Progress
General Angiology, Neurology and Aesthesiology
vaibhavpatel1028@gmail.com September 2, 2024
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
General Angiology
Introduction to Angiology
- Definition: Angiology is the study of the circulatory system, including arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels.
- Focus: Preventing, diagnosing, and treating lymphatic and blood vessel related diseases.
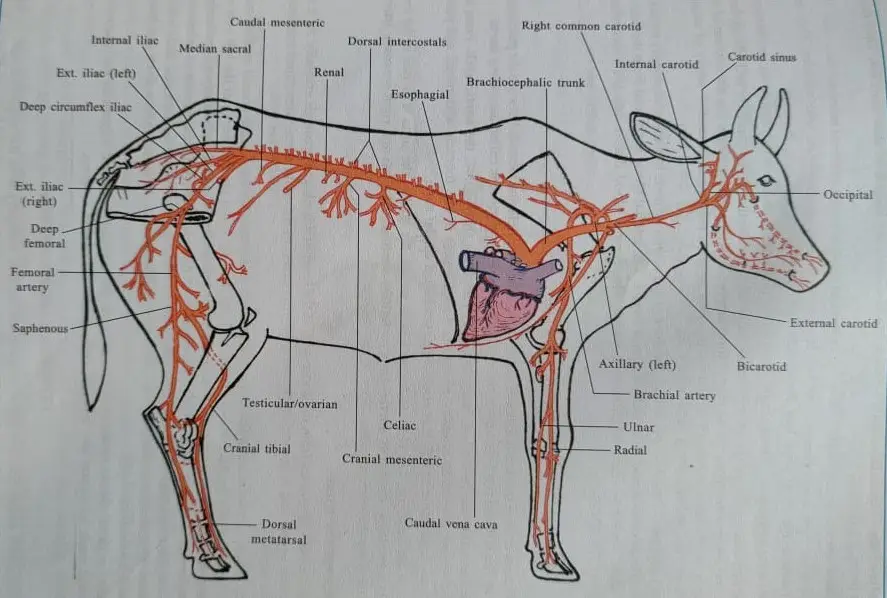
Structure of the Heart
- Components:
- Four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle.
- Heart valves: tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves.
- Function: Pumps blood throughout the body, maintaining circulation.
General Plan of Circulations
- Systemic Circulation:
- Oxygenated blood is pumped from the left ventricle through the aorta to the body.
- Deoxygenated blood returns to the right atrium.
- Pulmonary Circulation:
- Deoxygenated blood is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs via pulmonary arteries.
- Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium through pulmonary veins.
Lymphatic System
- Function: Transports lymph, a fluid containing white blood cells, and plays a role in immune function and fluid balance.
- Components: Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymph fluid.
Venous System
- Function: Returns deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart.
- Components: Deep veins, superficial veins, and venous sinuses.
Vascular Diseases
- Arterial Diseases: Narrowing, occlusion, dilatation or weakening of arteries, often due to atherosclerosis.
- Lymphatic Diseases: Lymphedema caused by reduced lymph transport and accumulation of lymph and proteins.
- Microcirculation Anomalies: Changes in temperature and color of skin, sometimes with pain, such as in Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Vascular Medicine
- Vascular Exams: Duplex ultrasound, contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), angiography, Doppler, plethysmography, tcPO2, capillaroscopy, functional testing (treadmill), and lymphofluoroscopy.
- Interventional Angiology: Percutaneous, x-ray-based endovascular catheter interventions for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Introduction to Neurology
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Components: Brain and spinal cord.
- Function: Processes sensory information and coordinates body functions.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Components: Nerves outside the CNS.
- Divisions:
- Somatic Nervous System: Controls voluntary movements.
- Autonomic Nervous System: Regulates involuntary functions.
Autonomic Nervous System
- Divisions:
- Sympathetic Division: Prepares the body for “fight or flight” responses.
- Parasympathetic Division: Manages “rest and digest” functions.
Sense Organs
- Function: Detect environmental stimuli and send signals to the brain.
- Includes: Eyes (vision), ears (hearing), nose (smell), tongue (taste), and skin (touch).
Formation of Spinal Nerve
- Process: Formed by the union of sensory (dorsal) and motor (ventral) nerve roots from the spinal cord.
Structure of Meninges
- Layers:
- Dura Mater: Tough outer layer.
- Arachnoid Mater: Middle layer with a web-like structure.
- Pia Mater: Delicate inner layer that adheres to the brain and spinal cord.
Structure of the Brain
- Regions:
- Cerebrum: Responsible for higher brain functions (thought, memory).
- Cerebellum: Coordinates movement and balance.
- Brainstem: Controls basic life functions (breathing, heart rate)
Point wise shorts notes
General Angiology
Introduction to Angiology
- Definition: Study of the circulatory system (arteries, veins, lymphatic vessels).
- Focus: Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of vascular diseases.
Structure of the Heart
- Components:
- Four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle.
- Valves: tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, aortic.
- Function: Pumps blood throughout the body.
General Plan of Circulations
- Systemic Circulation: Oxygenated blood from left ventricle to the body; deoxygenated blood returns to right atrium.
- Pulmonary Circulation: Deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs; oxygenated blood returns to left atrium.
Lymphatic System
- Function: Transports lymph (contains white blood cells); plays a role in immune function and fluid balance.
- Components: Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes.
Venous System
- Function: Returns deoxygenated blood to the heart.
- Components: Deep veins, superficial veins, venous sinuses.
Vascular Diseases
- Arterial Diseases: Atherosclerosis, narrowing, occlusion.
- Lymphatic Diseases: Lymphedema.
- Microcirculation Anomalies: Changes in skin temperature and color.
Vascular Medicine
- Exams: Duplex ultrasound, angiography, Doppler, plethysmography.
- Interventional Angiology: Endovascular catheter interventions.
Introduction to Neurology
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Components: Brain and spinal cord.
- Function: Processes sensory information; coordinates body functions.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Components: Nerves outside the CNS.
- Divisions:
- Somatic Nervous System: Voluntary control.
- Autonomic Nervous System: Involuntary control.
Autonomic Nervous System
- Divisions:
- Sympathetic Division: “Fight or flight” response.
- Parasympathetic Division: “Rest and digest” functions.
Sense Organs
- Function: Detect stimuli; send signals to the brain.
- Includes: Eyes (vision), ears (hearing), nose (smell), tongue (taste), skin (touch).
Formation of Spinal Nerve
- Process: Union of sensory (dorsal) and motor (ventral) nerve roots.
Structure of Meninges
- Layers:
- Dura Mater: Tough outer layer.
- Arachnoid Mater: Middle layer.
- Pia Mater: Delicate inner layer.
Structure of the Brain
- Regions:
- Cerebrum: Higher brain functions (thought, memory).
- Cerebellum: Movement coordination.
- Brainstem: Basic life functions (breathing, heart rate).

